Companies can use internal or external auditors to manage their environmental audits depending on their in-house resources and the role and intention of the audit. Risk elements are 1 inherent risk 2 control risk 3 acceptable audit risk and 4 detection risk.
Below is a list of the most important types of risk for a financial analyst to consider when evaluating investment opportunities.
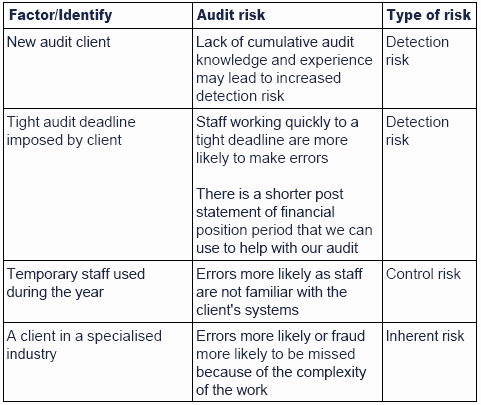
. The audit risk model is best applied during the planning stage and possesses little value in terms of evaluating audit performance. The first is control risk which is the risk that potential material misstatement would not be detected or prevented by a clients control systems. Dont let payroll fraud derail your business.
The external auditor has no connection to your business eg not an employee. A detection risk is a type of audit risk that results from poor planning. This type of audit involves working with other auditors or teams like financial auditors or performance auditors.
Three types of audit materiality include overall materiality overall performance materiality and the specific materiality. Types of Audit Risks Inherent Risks. Both have their place depending on what you want to achieve in.
This is the risk that the work carried out by the auditor does not uncover a material misstatement that exists. An inherent risk is the type of audit risk that cannot be identified by a companys internal auditors or. Majorly Substantive procedures are performed by the Auditor with the main aim of detection of material fraud or monetary misstatement at different assertion level in a company.
The risks are classified into three different types. The auditor did not sufficiently investigate a significant balance. Some audits have special administrative purposes such as auditing documents risk or performance or following up on completed corrective actions.
Accordingly the auditor controls audit risk by adjusting detection risk according to the assessed levels of inherent and control risks. An external audit is conducted by a third party such as an accountant the IRS or a tax agency. Are common types of specific audit.
A control risk is. PoliticalRegulatory Risk The impact of political decisions and changes in regulation. In the context of an audit this is a risk of misstatements in the audit itself.
Evaluate risk management policies and procedures. The external audit refers to the audit firms that offer certain auditing services including Assurance Service Consultant Service. You may also be asked to perform an audit of a particular system after unusual and suspicious activity is observed and reported.
An audit can apply to an entire organization or might be specific to a function process or production step. The audit procedures investigate financial statements with supporting documentation to see if they are error free. Specific Audit Cash audit Cost audit Standard audit Tax audit Interim audit Audit in depth Management audit Operational audit Secretarial audit Partial audit Post vouch audit etc.
The types of audit evidence include analytical procedures confirmations inquiry inspecting records inspecting assets observation recalculation and reperformance. There are three types of audit risk. Audit materiality provides the opportunity to the user of the financial statement auditor and the company.
The procedures used may have been inappropriate or misinterpreted. There are 8 types of audit evidence. 14 Types of Audits and Level of Assurance 2021 1 External Audit.
The three different types of. An independent company a customer or an internal person. The second is detection risk which is the risk that the audit procedures used are not capable of detecting a material misstatement.
An audit risk model is a conceptual tool applied by auditors to evaluate and manage the overall risk encountered in performing an audit. A full environmental audit will likely include a full environmental risk assessment similar to the one you see below. Systematic Risk The overall impact of the market.
Inherent risks Control Risks and Detection Risks. An inherent risk is the risk of material misstatements due to fraud or incompetence. Types of Audit Risk.
Auditors must use a combination of these audit procedures to obtain sufficient appropriate audit evidence. There is a chance an auditor. Detection risk can be split into sampling non-sampling risk.
In the context of an audit this is a risk of misstatements in the audit itself. Risk-based approach is the technique that auditors use in performing the audit in which they focus on analyzing and managing different types of risks that could lead to material misstatement. So its a significant risk especially for small businesses where there are usually fewer controls.
We will discuss this in detail below. Its one of the most common types of employee fraud according to the ACFE it occurs in 27 per cent of businesses and lasts for an average of 36 months. Unsystematic Risk Asset-specific or company-specific uncertainty.
The probability of a material error in the estimates of an account without taking into account the internal control. Clients and Auditors themselves. Detection risks This means that the auditor fails to detect the misstatements and errors in the companys financial statement and as a result.
I talked about the different types of audits as they relate to who is doing the ISO 9001 audit. When it comes to an internal audit there are two different ways of auditing the processes of your QMS. Horizontal auditing and vertical auditing.
The auditor uses these as per the different situations prevailing in the company. There are three common types of audit risks which are detection risks control risks and inherent risks. Audit risk Represents the risk of auditor failure to adjust his or her report appropriately to reflect any material misstatement of the financial statements.
Audit risks come from two main different sources. In this approach auditors direct their attention to those key risk areas of financial statements that may contain misstatement. Different Types of Audit Test 1- Audit Substantive tests.
In relating the components of audit risk the auditor may express each component in quantitative terms such as percentages or non-quantitative terms such as very low low moderate high and maximum. Audit consists of three components of risk are. A comprehensive environmental risk assessment like this enables the auditor to assess and.
And external auditors must follow generally accepted auditing standards GAAS.
9 Different Types Of Audits Internal External Financial More
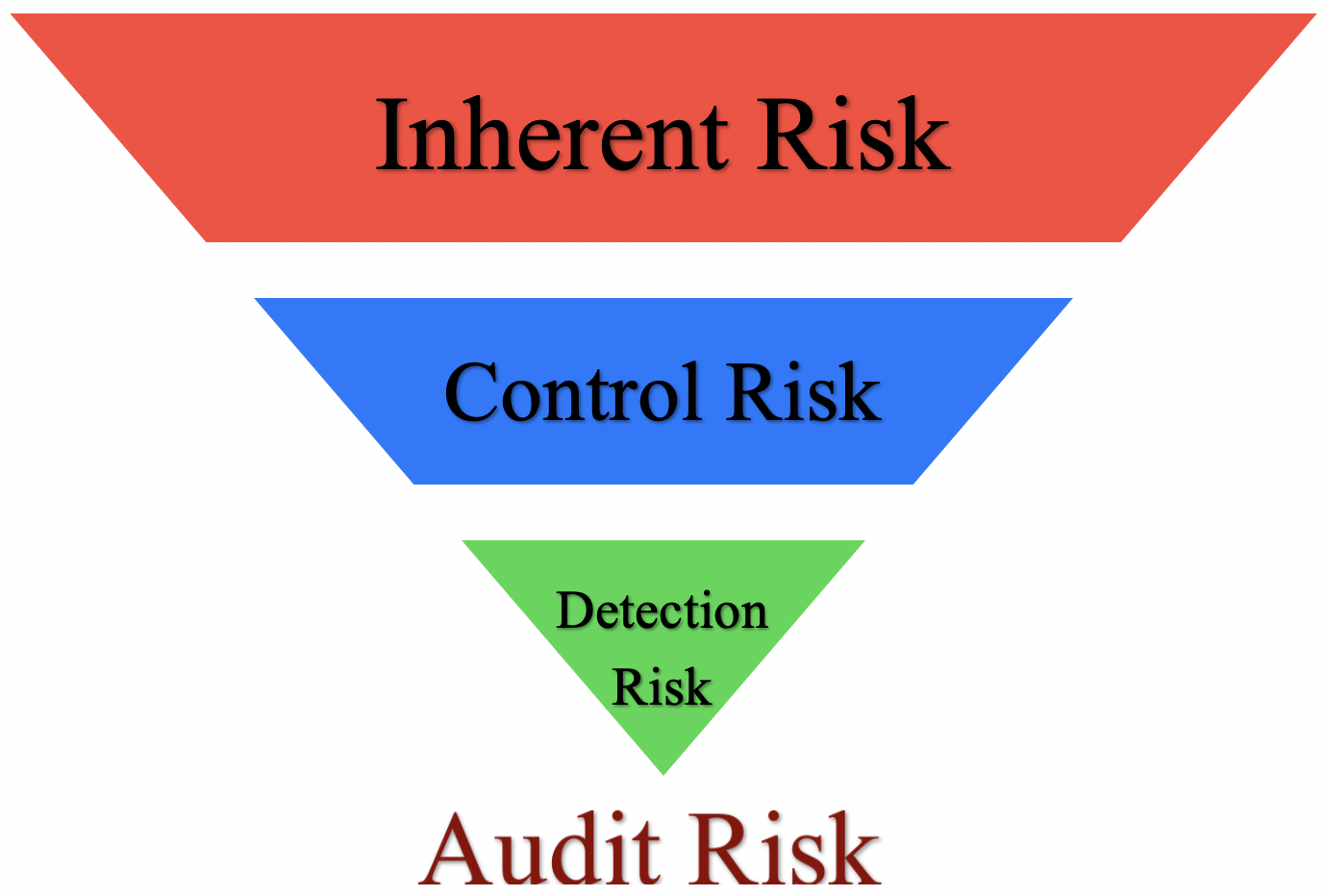
3 Types Of Audit Risk Inherent Control And Detection Accountinguide

0 Comments